
Global economic activity is picking up after an unprecedented decline this year due to the coronavirus pandemic, but a second major wave of infections could trigger more disruptions, the International Monetary Fund's top official said.
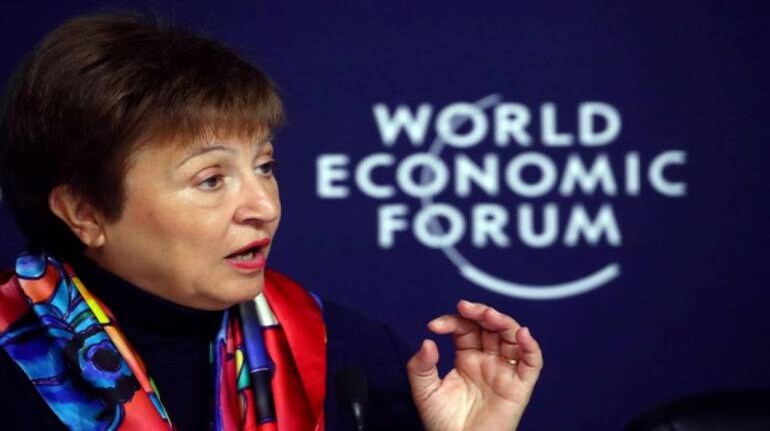
IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva said the fiscal costs of actions aimed at containing the pandemic and mitigating its economic fallout were driving up already high debt levels, but it was premature to start withdrawing needed safety nets.
"We are not out of the woods yet," she said in a blog posting ahead of Saturday's virtual meeting of finance ministers and central bank governors from the Group of 20 major economies.
The IMF last month further slashed its 2020 global output forecasts, predicting a 4.9 percent contraction and weaker-than-expected recovery in 2021.
Georgieva said $11 trillion in fiscal measures by G20 members and other countries, as well as massive central bank liquidity injections, have put a floor under the global economy.
Even so, dangers lurked, she said, including a major new wave of infections, stretched asset valuations, volatile commodity prices, rising protectionism and political instability.
Some countries lost more jobs in March and April than had been created since the end of the 2008 global financial crisis, and many of those jobs will never return, Georgieva said.
Job losses, bankruptcies and industry restructuring could pose significant challenges for the financial sector, including credit losses to financial institutions and investors, she said.
To ensure stability, continued coordination across central banks and support from international financial institutions was essential, she said. Regulation should also support the flexible use of capital to keep credit lines open for businesses.
"Monetary policy should remain accommodative where output gaps are significant and inflation is below target, as is the case in many countries during this crisis," she said.
In a report to the G20, the IMF warned that rising protectionism and renewed trade tensions endangered the recovery.
A weak recovery itself raised the chances of disinflation and a prolonged period of low interest rates, which could undermine debt sustainability and financial stability, it said.
Follow our full coverage of the coronavirus pandemic here.
Discover the latest business news, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!